Intel CPU Roadmap for 2024-2026: Arrow Lake, Lunar Lake, and Panther Lake
Intel, a powerhouse in the computing world, is charting an ambitious course for the future of its CPU technology. Let’s dive into their roadmap, showcasing a blend of innovation and performance upgrades set to redefine computing standards.
Intel CPU Roadmap 2024-25
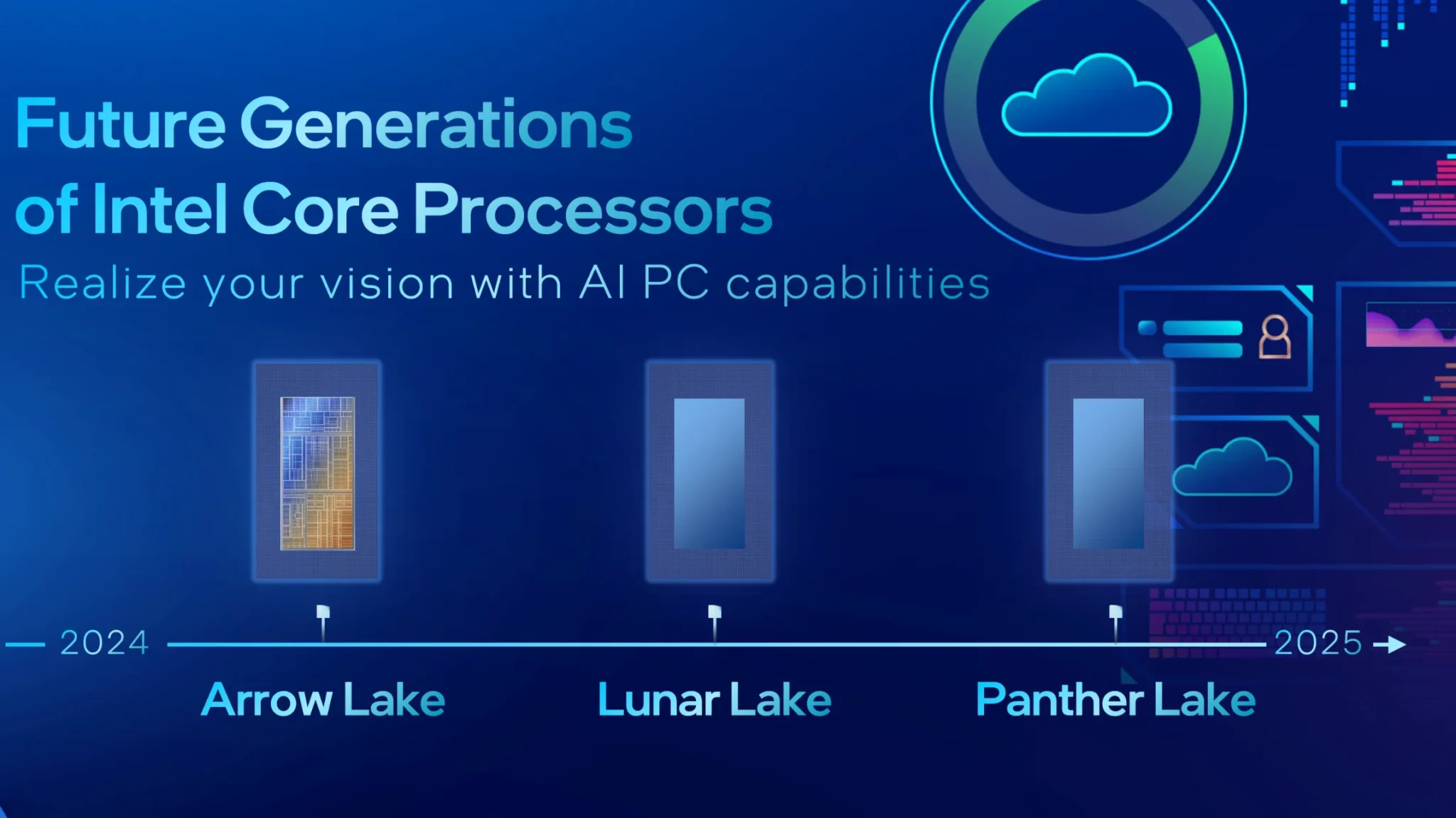
The 15th Gen Arrow Lake processors mark a significant step forward on Intel’s CPU roadmap. Following the Meteor Lake series, Arrow Lake will embrace a chiplet architecture featuring a 2nm-class 20A CPU die.
This evolution brings upgraded cores – Lion Cove (P) and Skymont (E) – enhancing processing capabilities. The integrated GPU (iGPU), based on the Battlemage graphics IP, will be fabricated on TSMC’s 3nm/4nm node, promising notable graphical improvements. Expect the desktop lineup, with up to 24 cores (8P + 8E), to debut in late 2024.
The 16th Gen family will build upon Arrow Lake, boosting core counts and cache sizes, reminiscent of the Raptor Lake refresh strategy. The flagship desktop model could sport an impressive 40 cores, including 8P and 32 E-cores. This iteration, scheduled for late 2025, will maintain the established process node and core architectures.
Lunar Lake, designed for ultrabooks and convertibles, will succeed the Lakefield lineup. Fabricated on TSMC’s 3nm (N3B) node, it promises a blend of efficiency and performance with up to 4P and 4E cores (+2 LP cores) and a lower TDP of 7-15W. Its launch aligns with the Arrow Lake timeline.
See also: AMD CPU Roadmap
Intel CPU Roadmap 2025-26
The 17th Gen Panther Lake series, set for the end of 2025, will be a mobile-centric design based on the Intel 18A node. It will introduce “Cougar Cove” P cores and “Darkmont” E cores, featuring a new die layout with up to 12 cores (4P, 8E, and 4LP). Panther Lake promises to combine mobility with power, suitable for the next generation of portable devices.
Finally, the 18th Gen Nova Lake, planned for late 2026, stands as Arrow Lake’s true successor. It’s expected to boast 16 P-cores and 32 E-cores (+4 LP-cores) on the Intel 14A node. Notably, these CPUs will include Rentable Units in P-cores and Arctic Wolf E-cores, along with high-cache variants akin to AMD’s 3D V-Cache chips. This lineup could set new benchmarks in CPU performance and efficiency.
Intel’s roadmap through 2026 paints a picture of a company not just keeping pace with technological advances but actively pushing the boundaries. From enhancing power efficiency in ultrabooks to ramping up core counts for desktop power users, Intel is addressing a broad spectrum of computing needs.
This vision is a testament to Intel’s commitment to innovation and its ability to adapt to the ever-evolving demands of the tech world. As these processors roll out, they’re set to offer consumers and professionals alike new levels of computing performance, opening up possibilities for advancements in various fields.
For those looking to become a business broker or advance in the tech industry, keeping an eye on these developments is essential, as they signal the direction in which the computing world is heading.
