AMD CPU Roadmap: Zen 5 and Zen 6 CPU core designs
AMD, a key player in the computing industry, has exciting plans for its future x86 CPU architectures. Recently, leaked internal slides revealed details about AMD’s upcoming Zen 5 and Zen 6 CPU cores, poised to power the Ryzen 8000 and Ryzen 9000 series processors.
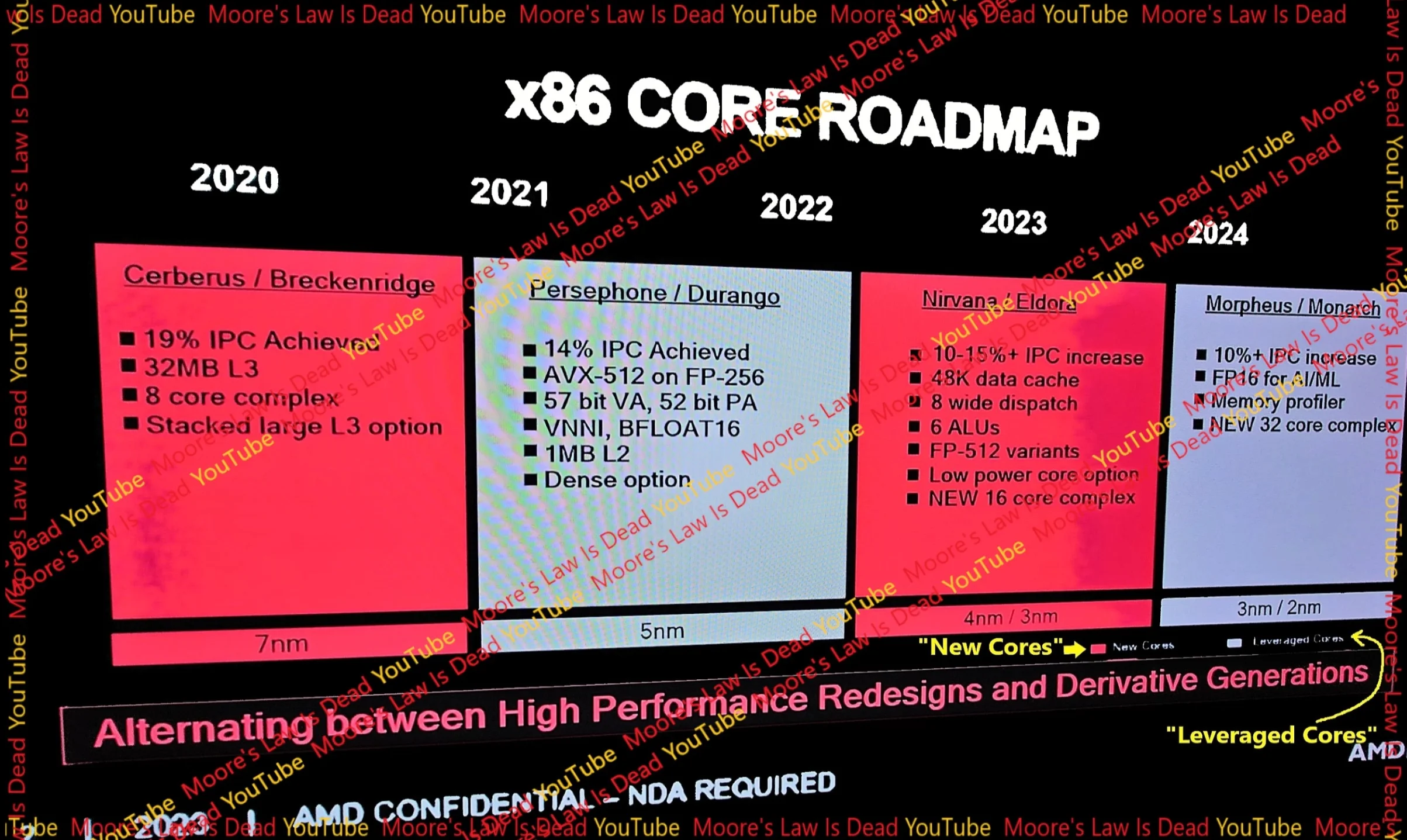
Zen 5: A Leap in Performance and Efficiency
With its Zen 5 CPU core design, codenamed Nirvana, AMD is targeting IPC (Instructions Per Cycle) gains above 10-15%. This leap is part of AMD’s broader strategy to increase the power efficiency of its CPU cores, offer larger data caches, and introduce new FP-512 features in the core design. The use of 4nm/3nm silicon in Zen 5 CPUs underlines AMD’s commitment to advancing semiconductor technology.
One of the standout improvements in Zen 5 is expected to be a dramatic increase in AVX performance, potentially leading to much higher Cinebench scores, a popular benchmarking tool. This would be a significant win for AMD’s marketing, given Cinebench’s wide usage.
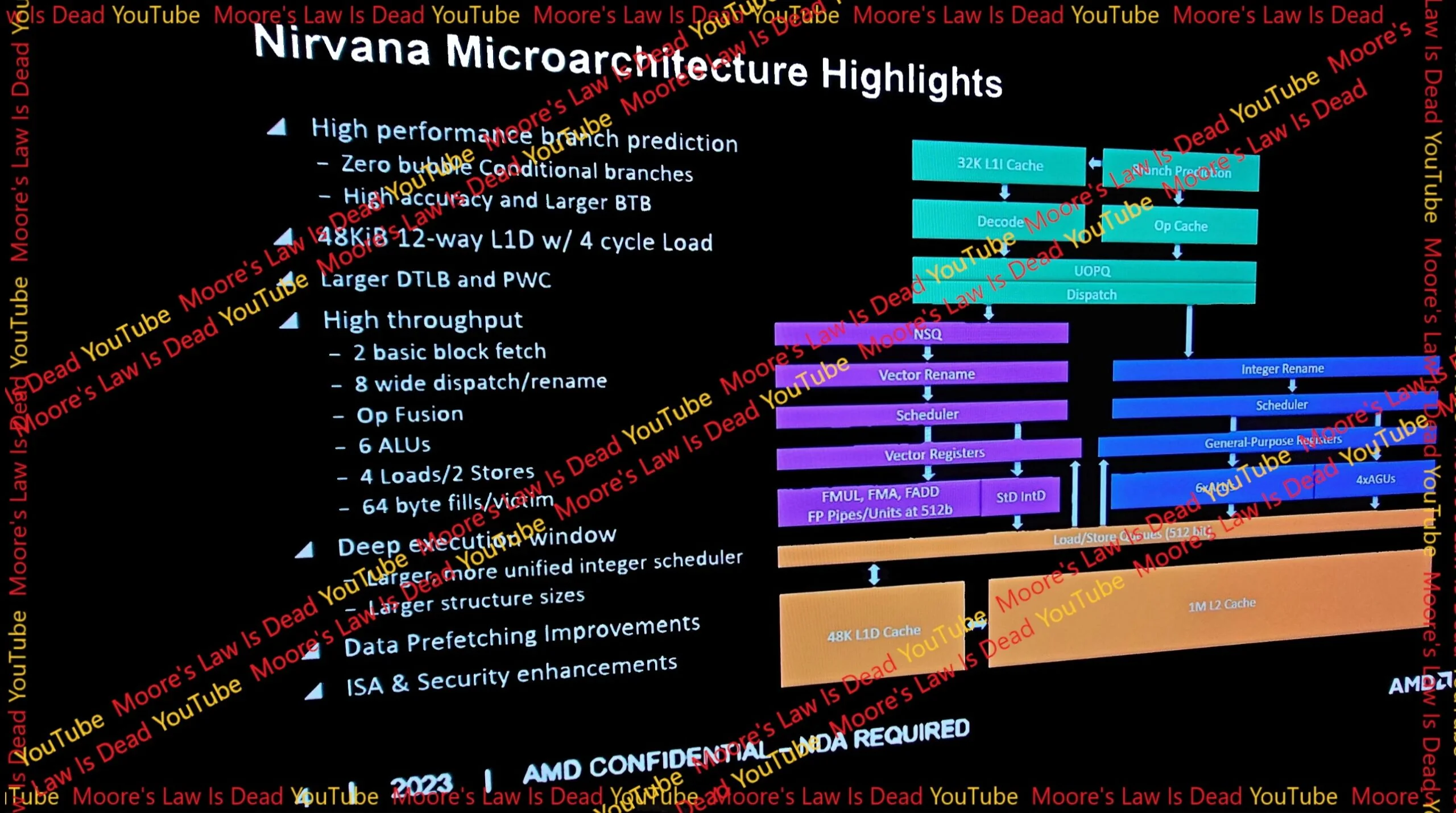
The Zen 5 architecture also plans to introduce new 16-core complexes, likely for Zen 5c CPU cores. This approach may lead to a variety of configurations in the Ryzen 8000 series, including hybrid models similar to Intel’s approach, offering up to 32 Zen 5c cores.
See also: Intel CPU Roadmap
Zen 6: Pushing the Boundaries Further
Zen 6 aims for a 10+% IPC gain over Zen 5, using 3nm/2nm silicon and adopting a new multi-die structure. This structure will fully embrace die stacking, potentially stacking CPU cores on top of an I/O die. The expected benefits include dramatically reduced latency, thanks to AMD’s new Infinity Fabric and fast silicon interconnects. AMD’s goal with Zen 6 is to achieve monolithic performance from chiplet-based designs, which could significantly impact latency-sensitive workloads like gaming.
Zen 6 plans to offer CPU core complexes with up to 32 total cores, paving the way for massive Zen 6 EPYC processors, a boon for data centers and high-performance computing.
AMD Ryzen 8000 “Granite Ridge” Desktop CPUs With Zen 5 In Late 2024
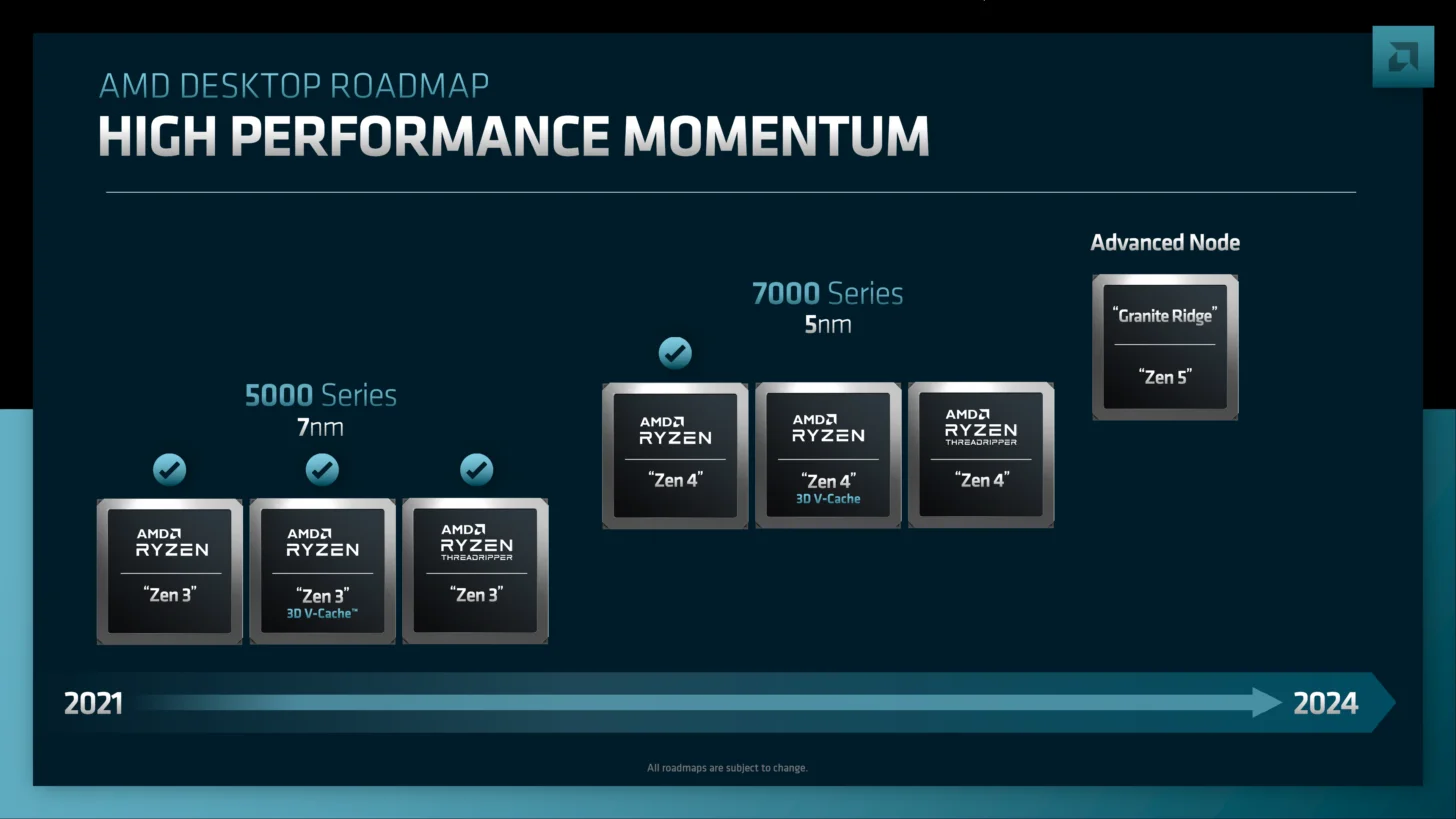
The successor to the AMD Ryzen 7000 series, codenamed Raphael, will be the Ryzen 8000 series, known as Granite Ridge. These chips will utilize a mix of 4nm and 6nm nodes, with the 4nm process for the CCD and the 6nm for the IOD.
Granite Ridge is expected to launch in late 2024, as AMD continues to optimize its Zen 4 cores for the desktop segment. This transition marks a significant step in AMD’s CPU evolution, combining advanced node processes for optimal performance and efficiency.
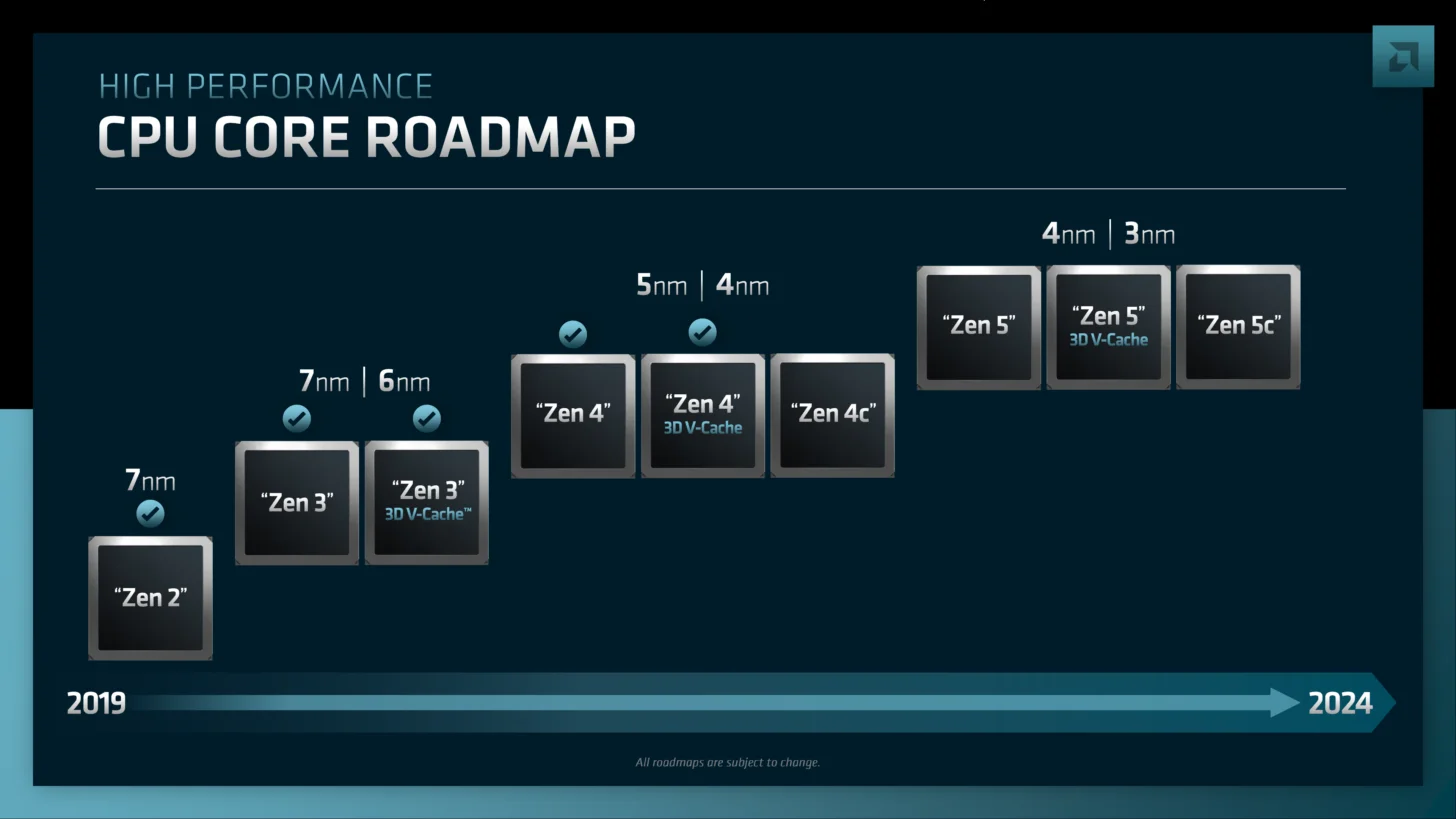
Zen 5 architecture, launching in 2024, promises a completely new microarchitecture designed from the ground up. It focuses on delivering enhanced performance and efficiency, a re-pipelined front-end, and a wide issue.
Notably, it integrates AI and machine learning optimizations, a feature set to significantly impact computing capabilities. Zen 5 CPUs will come in three flavors: Zen 5, Zen 5 V-Cache, and Zen 5C, each tailored to specific performance and efficiency needs.
AMD Threadripper 8000 “Shimada Peak” HEDT CPUs With Zen 5 In 2025
Looking further ahead, AMD’s plans for the high-end desktop (HEDT) market are equally ambitious with the “Shimada Peak” chips set to replace the Storm Peak chips in the Threadripper 7000 family, due for launch later this year. These next-generation HEDT CPUs are expected to retain the same socket designs while offering a significant performance leap, courtesy of the new Zen 5 cores and a brand new cache design.
AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper 7000 CPUs could feature up to 96 cores, showcasing AMD’s commitment to pushing the limits of processor technology. Accompanied by the latest DDR5 and PCIe Gen 5 standards, these CPUs are poised to redefine high-performance computing.
In summary, AMD’s roadmap through 2024 and beyond is shaping up to be a thrilling journey in processor technology, with Zen 5 and Zen 6 poised to bring groundbreaking advancements in performance, efficiency, and computing capabilities.
